HOW DO PLANTS
DEFEND THEMSELVES
To prevent further spread of infection, healthy
plant cells around the site of infection will die.
Ø Plant defense mechanism
ü Structural
defense
Physical barriers that inhibit
pathogens from entering into the host cell
ü Chemical
defense
Ø Preexisting structural defenses
I.
Amount and quality of wax and cuticle
II.
Structural of epidermal wall
III.
Size,
location and shapes
of stomata and lenticels
IV.
Thick
walled cells – hinder the advance of the pathogen
Example
of natural waxes on leaf and fruit

Leaf
tissue anatomy
Induced structural defense :
a.
Cytoplasmic defense reaction
|
·
Some cytoplasm will surround the mass of hyphae
|
b.
Cell wall defense structures
|
·
Morphological changes of cell wall structures such as swelling, cell
wall thicken and callose papillae
|
c.
Histological defense structures
|
·
Formation of cork layer
·
Formation of abscission layer
·
Formation of tyloses
·
Deposition of gums
|
d.
Necrotic defense reaction
|
·
Hypersensitive response
|
Formation
of cork layers
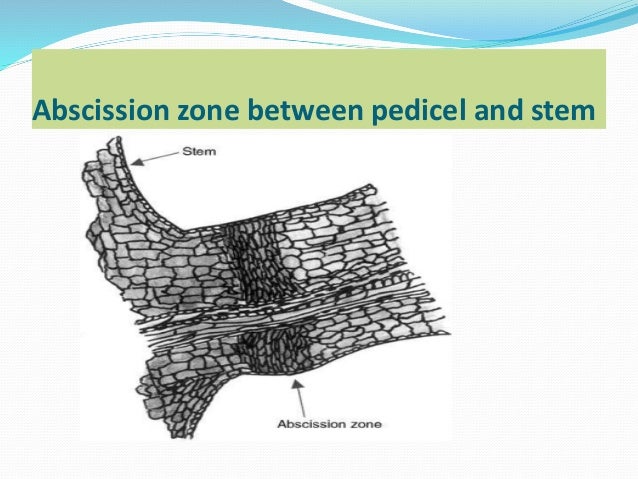
Formation
of abscission layers
Formation
of tyloses
Formation
of gums
Ø Preexisting chemical defense
Inhibitor
released by the plant in its environment is
Fungitoxic exudates- inhibit germination of spores, while inhibitors
present in plant cells before infection are Phenolic compound, saponins Hyrolytic
enzymes,
Induced
biochemical reaction :
a) Hypersensitive
response
Induced the death of
host plant cell at the site of infection. Limit the growth of pathogen
b)
Active oxygen radiacals
Distrupt the cell
membrane
c)
Strengthening molecules
Reinforcement of cell
wall
d)
Antimicrobial substances
To kill the pathogen
e)
Immunization of plants against
pathogen
Defense through
plantibodies
f)
Local and systematic acquired
resistance
Induction of plant defenses by
artificial inoculation with microbes or treatment with chemicals which is Local acquired resistance and Systemic acquired resistance
REFERENCES :
prepared
by : Tuan Muhamad Shaiful Nizam Bin Tuan Aziz (Agronomy Student), UiTM






No comments:
Post a Comment